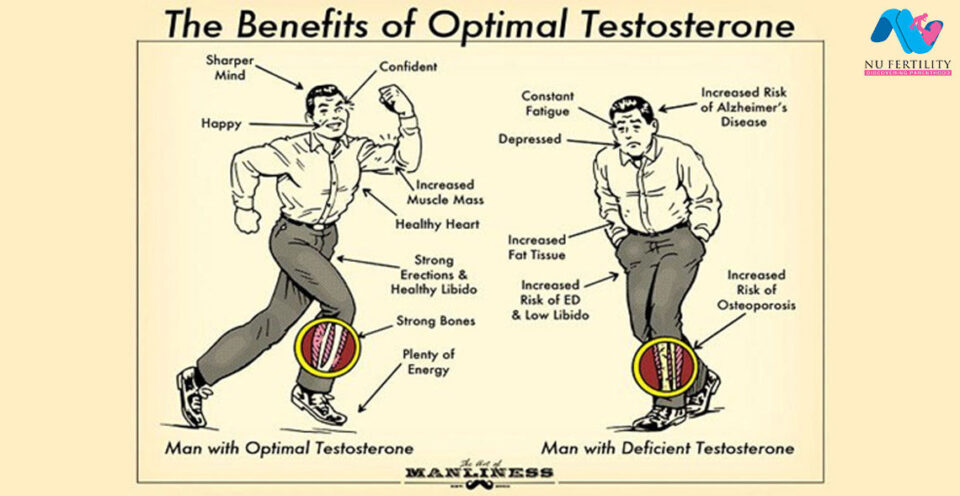
Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone and is a type of hormones called androgens. Testosterone is present in the bodies of both men and women but it plays a more important role in men. It is created in a large amount in a man’s body and is responsible for a lot of ‘masculine’ features and sex-specific characteristics. A man’s body produces testosterone in the testicles where sperm is produced.
What are normal ranges or levels of testosterone in men?
A low level of testosterone in men is around 300 nanograms per deciliter while the upper limit is around 1000-1200 ng/dl. The production of testosterone begins to accelerate during puberty and beings on a downward spiral after the age of 30.
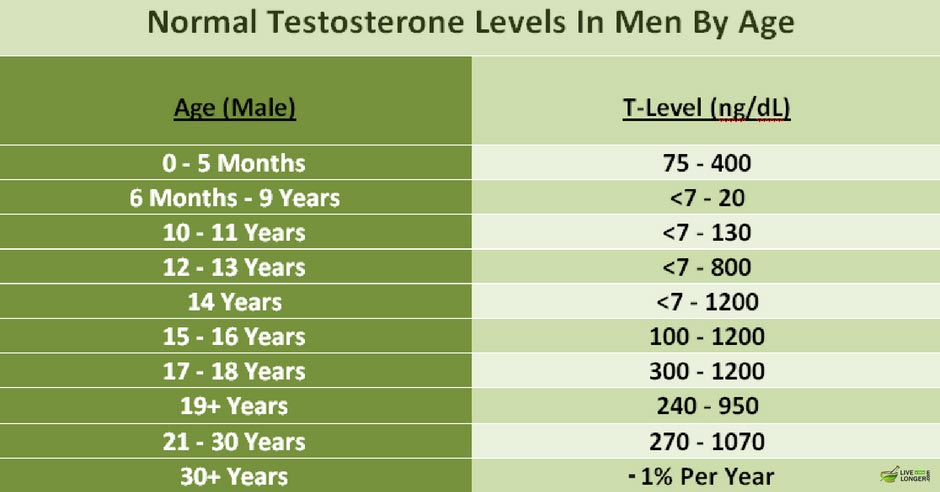
So there is no need to panic if you T-levels drop a little from the limit but if it drops at an expedited rate, you should seek professional help.
How Common is Low Testosterone in Men?
Research suggests that 2.1% of the male population may have low testosterone. Studies have also shown that the rate of average testosterone has been dropping by 1% every year in American men. This means that a 60-year-old man in 2002 had 17 per cent more testosterone than a 60- year-old man in 2019. Of course, the odds of suffering from Low T is increased if a man is overweight, has diabetes or has a poor lifestyle.
Symptoms of low testosterone
What are signs that you might have low testosterone? There are many symptoms of low testosterone and it’s possible that you only suffer from a few of them. Below are ten common signs of low testosterone:
1) Hair loss
According to the National Institutes of Health, Hair loss is a common problem with adult males in the USA and affects 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States. Many factors can contribute to male pattern baldness but if you find this to be happening to you, it’s best you check your T-levels. Testosterone is vital in the growth of your facial and body hair.
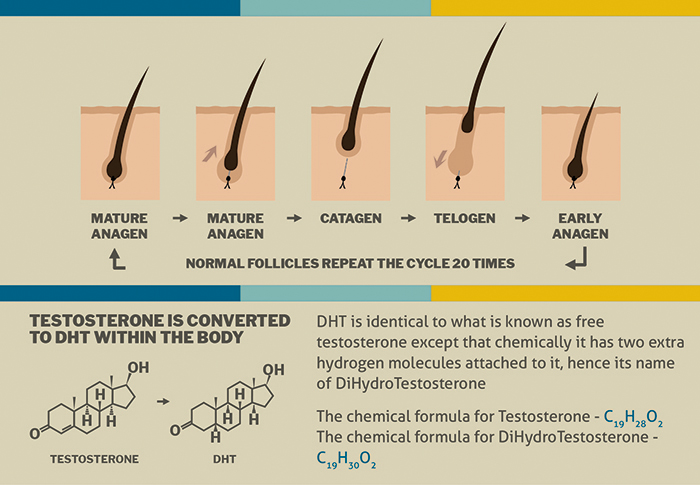
This is the science behind it- Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is created out of testosterone by an enzyme called 5-alpha-reductase. The DHT affects the functioning of the skin, hair follicles, and the prostate. While research on hair loss is still on-going, a link has been observed between the sensitivity of hair follicles to DHT and hair loss. The AR gene in your DNA is responsible for the sensitivity of hair follicles to DHT. If your follicles are highly sensitive, they will be easily affected by small amounts of DHT, leading to hair loss.
2) Low sex drive
Testosterone is majorly responsible for causing an active sex drive in men. So when your T-Levels are low, you will experience a noticeable drop in your libido than usual.
It will affect intercourse and masturbation in a way that sometimes you may not even think about it for a long period. And this issue will affect your partner as well. So if your sex drive is much lower than usual with no explanation such as stress, accidents or inadequate sleep, then it is highly likely that you are suffering from low libido.
3) Erectile dysfunction
Testosterone
aids in the release of nitric
oxide which is essential in the appearance and maintenance
of an erection. So inevitably when your T-levels are low, you will find it difficult to get and sustain erections. You will also experience fewer spontaneous erections than normal.
Another issue is that your sex drive will be lower than normal when you have low T-levels thus making it difficult to get erections. While the majority of ED cases are caused by other health problems, it’s possible that low testosterone can affect your sexual prowess.
4) Infertility
Low testosterone indirectly causes trouble with your fertility. Men with low testosterone can sometimes produce healthy sperm as the production of sperm is dependent on other hormones.
Low testosterone leads to a low sex drive that can result in a lack of desire for sex. Erectile dysfunction causes fewer and less effective erections which can make it difficult to reach climax which can hamper the process of conception.
If you and your partner are having trouble conceiving, you should have your testosterone levels checked among other things.
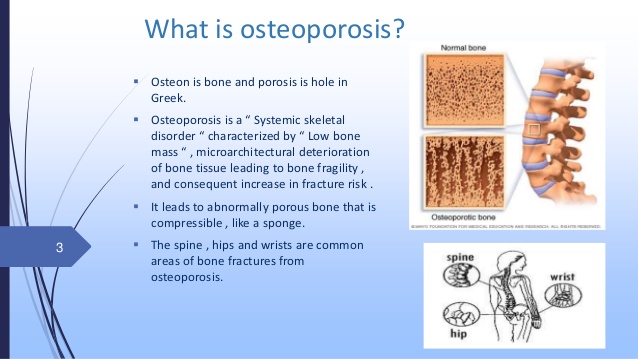
5) Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease that makes the bones fragile making them susceptible to bone fractures. It can be a cause of pain, disability, and depression, leading to a loss of independence and social isolation.
A
small amount of testosterone is converted
to estrogen to protect your bones. But if your body does not have enough testosterone, it will stop this process. This may lead to weak bones and osteoporosis in the worst case. You may have to undergo testosterone replacement therapy in case you are a man
diagnosed with this disease.
6) Low muscle mass
All of us know by now that testosterone is needed to build muscle and if you have low T-levels, your muscles will convert to fat or shrink from the usual size.
It
works like this- Muscle cells have androgen receptors that allow testosterone to bind to it and maintain its strength. Without adequate levels of testosterone, this functioning stops causing muscle degradation.
A
study published in the Curr
Diabetes Rev showed that obese men with
low testosterone had more fat deposits, especially in
the belly compared to healthy men. This is a vicious cycle as fat cells increase the production of an enzyme called aromatase. This converts testosterone to estrogen which in turn, causes fat to be deposited in your chest, hips, and thighs. Another way low
T-levels affect testosterone is by causing fatigue and lethargy which of course, will dissuade men from exercising!
7) Mood swings and irritability
You
must have seen the women in your life get moody and irritable when she’s on her period. But did you know that a man could get ill-tempered also because of hormonal issues?
A
study from 2012 showed
that hypogonadal men (men with low testosterone levels) felt comparatively more depressed and anxious to hypogonadal men seeking testosterone therapy.
The irritable male syndrome can cause anger, sadness, depression, anxiety, frustrated and a host of other mood issues. This not just affects you but also your family, friends and even your work. Some men can suffer from the symptoms of menopause such as hot flashes, sleep deprivation and irritability. But let’s not blame all mood issues on testosterone, a lot of factors like increasing age, sickness, medications, and stress can cause it. So if you find your mood to be suddenly altered, head over to your doctor to get checked.
8) Fatigue and difficulty concentrating
Optimum levels of testosterone help you feel energized and raring to go. Not having enough will impact your overall outlook for the day and your energy. Enough if you get enough sleep, you may still feel tired and unfocused. You will find it very difficult to be motivated to hit the gym with your reduced energy levels. So, low testosterone levels can contribute to fatigue and tiredness but, equally, lack of sleep can contribute to low testosterone levels. If you feel tired for weeks and if it can’t be explained by stress or external conditions, then low levels of testosterone may be responsible.
9) Memory Problems flashes
Testosterone
does more than provide a man with masculine features, it also helps brain function especially with memory. A
study published in the NCBI showed that men over the age
of 70 years had an age-related reduction in testosterone
levels and also suffered from cognitive decline. Do not be alarmed though, forgetfulness is a guaranteed sign of low testosterone. There could be many factors causing this issue. However, if you’ve noticed that your memory is poorer than usual and you are facing
several other symptoms discussed, then you should take notice.
10) Improper Sleep
The connection between testosterone and sleep is almost cyclical. If you have low testosterone in your body, you may not be able to get adequate sleep. And it is the other way round too if you are sleep deprived, your testosterone levels may drop.
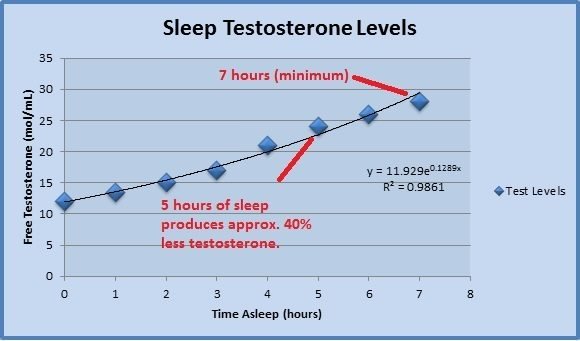
In a study conducted by the University of Chicago Medical Center, heathy men reported a decrease in testosterone by 10% to 15% after only a week of sleep restriction.
Causes of low testosterone
Low testosterone can usually occur due to a lot of factors. If your testosterone levels fall below 300 ng/dL that state is known as hypogonadism. The two basic types of hypogonadism are:
- Primary hypogonadism
- Secondary hypogonadism
Causes of both differ a lot and depend on different – different factors described below
Primary hypogonadism
Primary hypogonadism occurs when your testes do not produce enough testosterone. This can be due to a genetic defect or due to an accident or illness.
Inherited conditions include:
- Undescended testicles: In rare cases, the testicles do not descend from the stomach before birth
- Klinefelter’s syndrome: This is a condition in which a male is born with three chromosomes: X, X, and Y instead of the normal X and Y.
- Hemochromatosis: The presence of too much iron in the blood can lead to damage to the pituitaries and testicles.
Types of physical damage to the testicles include:
- Injury to the testicles due to vehicular accidents falls or force to that area
- Mumps orchitis is a kind of mumps infection
- Treatment for Cancer treatment: Chemotherapy or radiation can directly affect testosterone levels.
Secondary hypogonadism
Damage to the pituitary gland or hypothalamus can cause Secondary hypogonadism. These sections of the brain affect the performance of the testes, which of course produces testosterone.
Inherited or disease conditions in this category include:
- Pituitary damage due to drugs, kidney failure, or small tumours
- Kallmann syndrome is a disease that causes abnormal hypothalamus function
- Inflammatory diseases, such as tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, and histiocytosis
- HIV/AIDS
Acquired circumstances that can lead to secondary hypogonadism include:
- Ageing: A man’s testosterone levels will inevitably drop yearly after the age of 30.
- Excess Fat: Being overweight has such a negative impact on almost every function of the body including the production of hormones
- Medications: Being on anabolic steroids for a long time can affect the function of the pituitary gland.
- Prolonged illness: Physical stress after surgery or prolonged sickness can cause the reproductive system to shut down for a while.
How to test testosterone levels at home
Understanding accurate levels of your testosterone is quite important before taking any sort of step. Hence we suggest getting your testosterone levels lab tested. However, before spending money on lab tests, there are a few symptoms that can clearly show disturbed T- levels in your body. Some common symptoms that indicate low testosterone levels include:
• Depression disorder
• Low Self-confidence
• Lack of concentration
• Disturbed sleep
• Downfall in energy levels
• increased body fat and decreased muscle mass
• Low sex drive
• Osteoporosis/brittle bones/bone breaks
• Male boobs or Gynecomastia in men
• Soft voice
• Less hair all over the body in males
• Facial hair growth in women etc
It is quite clear that you can realize disturbed testosterone levels at home but cannot check your T-levels accurately. For that, you need to get yourself tested.
T – levels are measured by 2 different methods and both of them have their own units
Blood Test – This type of test involves taking a blood sample which is often collected through a blood draw (venipuncture). Unit of measure used in a blood test is nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL).
Saliva Test – Collecting a sample for this type of test is comparatively quite easy. For instance, you just need to spit into a tube for drawing a sample. Unit of measure used in the saliva test is picograms per millilitre (pg/mL).
How to compare these 2 tests?
Results derived from both these tests are different in numbers with different measuring units and hence they will look completely different. However, this does not mean that either of the tests is inaccurate, they are just 2 different methods. Usually, for comparison, 1 ng/dL is considered equivalent to 10 pg/mL. Results obtained can show very clearly whether you are low, normal or high on testosterone levels. Once you get to know your T-levels, you can take steps accordingly.
Physical Examination for diagnosing low testosterone
Low testosterone is easy to diagnose and is done through a simple blood test. The testosterone level in an average male’s blood should be between 300 ng/dL and 1,200 ng/dL. Your doctor may go ahead and conduct a physical exam to check your the growth of your hair, muscles and the size and appearance of your testicles.
A usual diagnosis will include:
- BMI to check for obesity
- Metabolic syndrome
- Overdeveloped breasts
- Testicles size and health
- Prostate size and functioning
Lab testing of T- levels
At your medical visit, your health history will be taken, and the doctor will do an exam and look for some of the signs and symptoms mentioned in this article
Your doctor may order these blood tests:
- Total testosterone level: This is usually done at 2 different times of the day.
- Luteinizing hormone test which may reveal a pituitary gland.
- Blood prolactin level to check for issues with your pituitary glands or the presence of tumours.
- Blood haemoglobin or Hgb.
Another way of measuring or testing your Test Levels is collecting the saliva sample as mentioned above already.
Questions to ask your doctor
- How much improvement can you see with testosterone therapy?
- What therapy would suit your lifestyle and budget?
- Will you need lifelong testosterone therapy?
- Will you face any side-effects of testosterone therapy?
How to treat low testosterone
Treating low testosterone works simply by adding testosterone in your bloodstreams in various forms. Here are the 6 ways to treat low testosterone:
- Gel – applied daily to a specified area of your skin
- Patch – applied once a day on any part of your skin
- Injection – injected every 2 to 4 weeks in a clinic or can be done at home by yourself
- Nasal gel – applied inside your nostrils
- Testosterone therapy or Implantation – placed right below the skin of your upper arm by a doctor and lasts for 3 to 6 months
- Testosterone boosters– contain vitamins and minerals that can boost your testosterone if your low-T isn’t caused by medical or genetic problems
How Effective Is Treatment For A Person With Low Testosterone?
You can stop feeling worried as adult young to middle-aged males with low T have a favourable chance of getting back to normal. However, older patients may not respond very well as well to treatment. Also, being diagnosed late when osteoporosis has already set in can make treatment tricky.
How Often Should A Man Have His Testosterone Levels Checked?
To be sure that nothing is wrong, you should get checked every 5 years after you turn 35. If you suspect that you are suffering from the above symptoms, its best to seek medical opinion immediately. Once you have begun seeking treatment, test your T-levels every couple of months to make sure the levels have not risen over the normal level.
Can You Prevent Fall In Testosterone Levels?
As we’ve discussed above, there are many factors that can be attributed to low testosterone. Genetic factors cannot be prevented and diseases like cancer cannot be predicted. What you can do is lead a healthy life, keep your weight in check, avoid smoking and taking drugs and live an active life. These changes can delay the onset of low testosterone.
Prevention is better than cure they say, hence its always better to understand, realize the cause and then act before taking any step further with less knowledge.